Estimation of Error Distribution for Multi-source Data without Ground Truth Data using Modified Appr
- Aug 24, 2017
- 1 min read
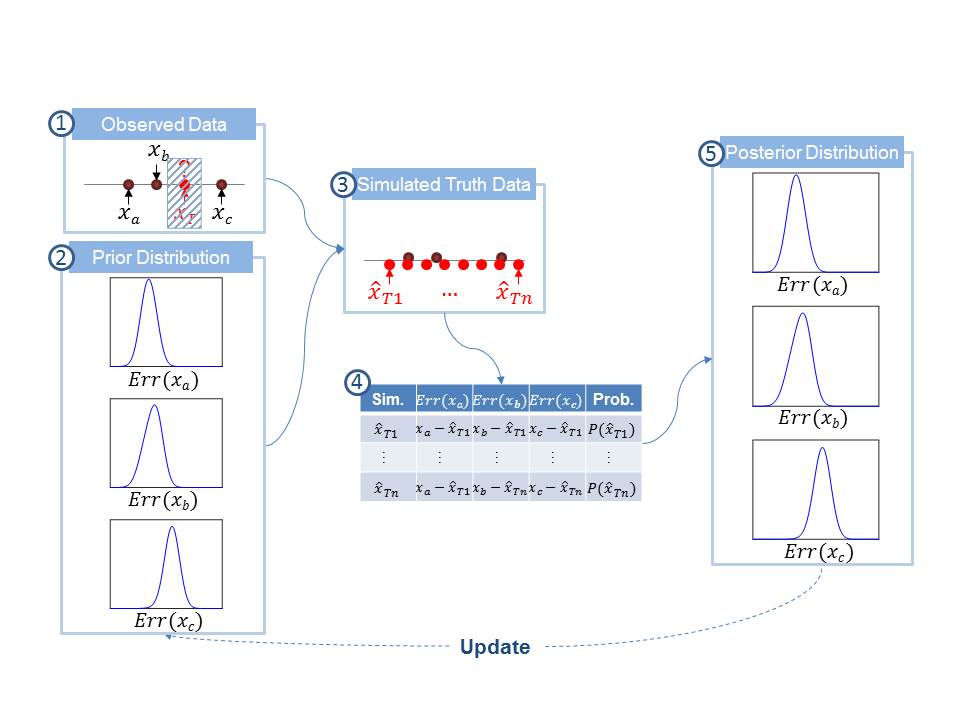
One of the challenges in measuring accuracy of multi-source data, before this study, is a requirement of ground truth data (or baseline data), since the accuracy of each data source is defined as the difference between the truth and the measurements of the data source. Determining the ground truth data source is another challenge since measuring the accuracy of the ground truth involves additional requirement of more accurate baseline data. This study proposes a methodology to estimate error distributions of data sources by aggregating measurements from multi-source data. Approximate Bayesian Computation was adopted and modified to construct the error distribution based on simulations. In the simulated experiment, the proposed model outperformed the alternative approach, which is a conventional way of evaluating data source that is gathering error information by using the benchmark data. The sensitivity analysis is also provided to explore the model performance by sample size, number of data sources, and distribution types. The proposed model is limited to one dimensional variable with an assumption of independence between the data sources, but the basic approach provided in this study might be easily expanded in other applications.























Comments